CBT Explained
What It Is
How It Works
What to Expect
Learn Why CBT Is
2X Faster and
3X More Effective
Than Traditional Talk Therapy.*
Take the first step toward real progress.
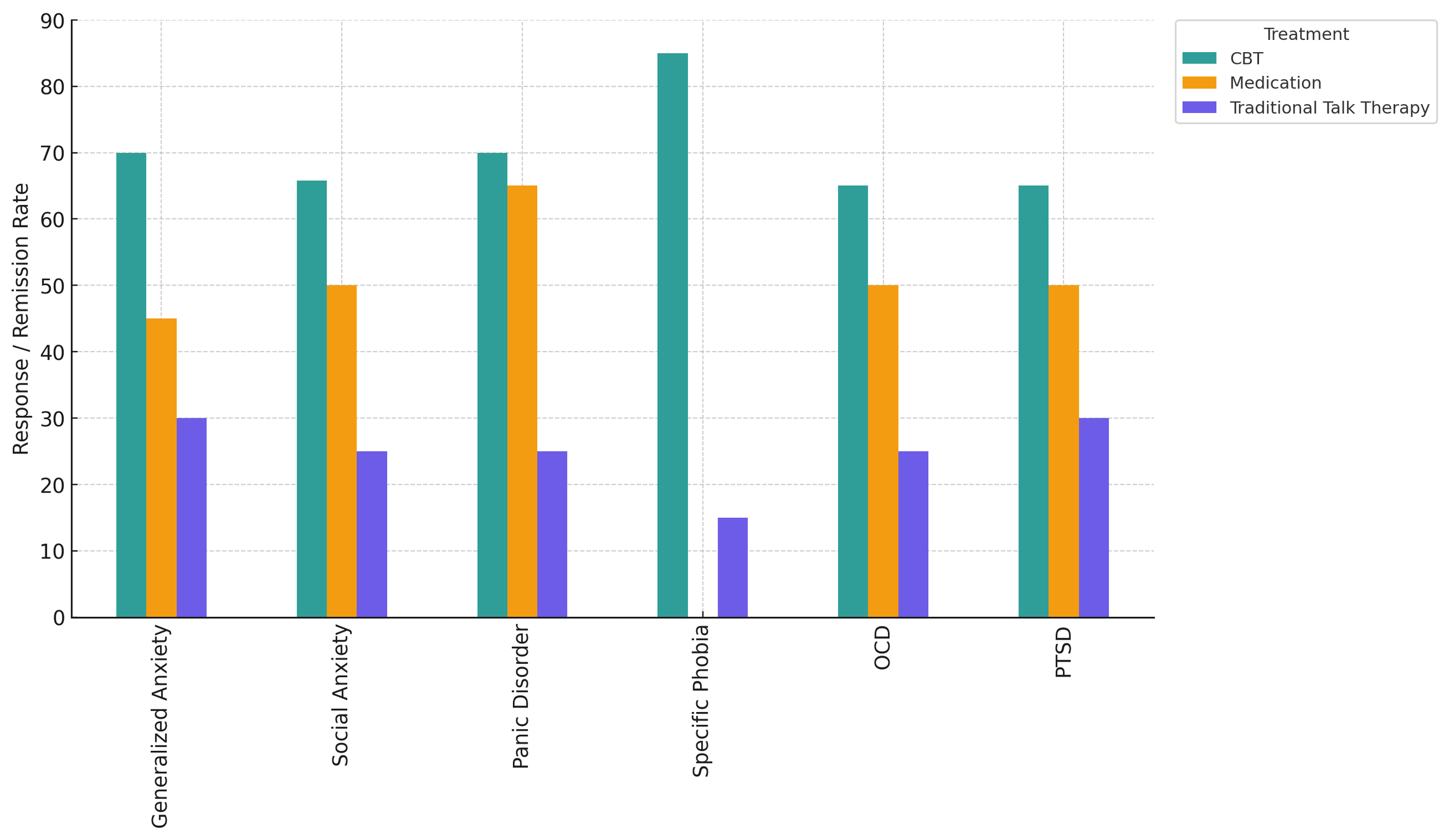
Why CBT Works
**Sources for this data available at the bottom of the page.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy helps you change thoughts and behaviors so your life changes, often in weeks, not years.
At CBT LA, doctoral-level psychologists deliver gold-standard Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Los Angeles and CBT telehealth across California, using clear plans, brief weekly actions, and visible milestones.
You’ll leave Session 1 with a plan. We co-design small, doable steps you can practice between sessions so progress starts right away.
Start Feeling Better This Week.
What Is CBT?
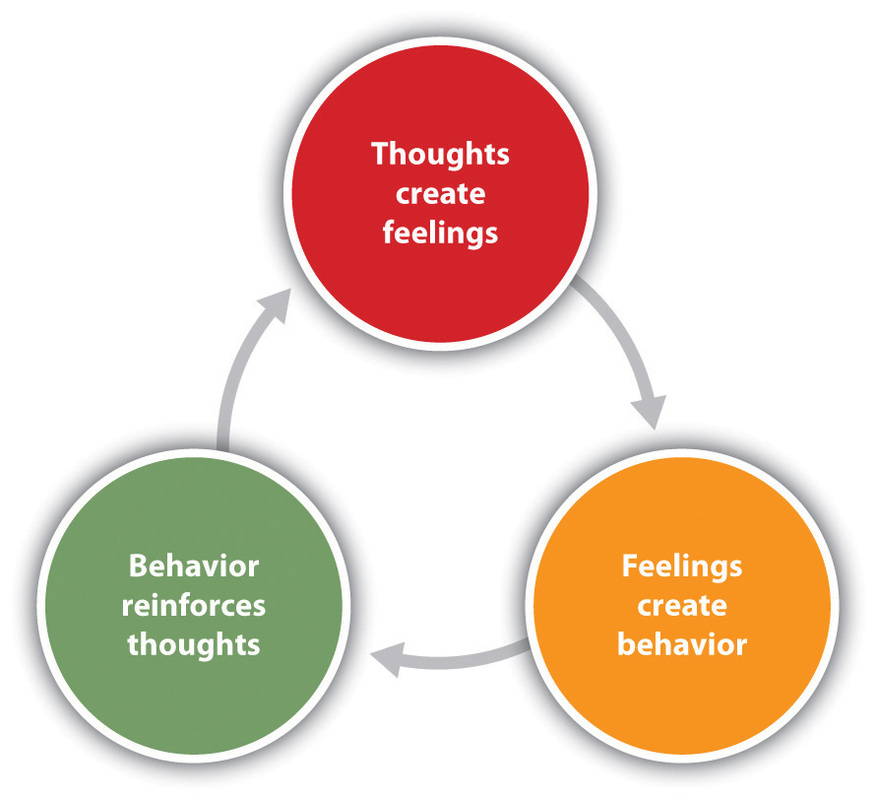
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based approach that changes unhelpful thought–emotion–behavior loops with structured skills you can practice between sessions.
CBT targets the here-and-now patterns that keep problems in place. Together we identify the loop (thoughts → feelings → behavior), run small experiments, and install habits that stick.
Structured & time-efficient: a clear roadmap with session milestones
Active & practical: brief home practices measured in minutes, not hours
Proven across conditions: recommended by leading clinical guidelines for anxiety, depression, OCD, PTSD, insomnia, couples issues, and more
Outcomes snapshot: Last year, most clients who completed 8–12 sessions reported meaningful improvement on standard assessment measures (e.g., sleep efficiency, depression, anxiety, etc.).
If your days are shaped by worry, low energy, poor sleep, or conflict cycles, CBT pinpoints the exact thoughts and behaviors maintaining those loops, then replaces them with skills you can practice in minutes.
What to Expect in Your First Session
Clarity fast: We map your goals and the exact loops (thoughts/feelings/behaviors) to target.
A concrete plan: You leave Session 1 with a personalized plan and 1–2 small, doable actions.
Next steps: You’ll begin learning practical skills and tracking progress by Session 2.
Typical Progress Milestones Help You See Change Happening
Session 2: Personalized roadmap + first micro-practice
Session 4: Early behavioral shifts (less avoidance; better sleep; first communication wins for couples)
Session 8: Measurable improvements (lower anxiety intensity; improved mood activation; more consistent focus for Adult ADHD)
Session 12 and Beyond: Consolidation + relapse-prevention plan you can keep
Most clients notice meaningful progress by weeks 4–8 with consistent practice.
Take the first step toward lasting change.
Why is CBT the Most Effective Treatment?
CBT is Goal-Oriented
Unlike a lot of talk therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy is a problem-solving therapy aimed at helping you achieve your goals. The goals can be anything from getting a job to finding a romantic partner to reducing feelings of anxiety or depression. Once you meet your goal, you and your therapist collaboratively decide whether there is anything remaining to work on or to end treatment.
CBT is Present-Focused
Cognitive behavioral therapy typically focuses on present difficulties and distressing situations. This here-and-now focus allows you to solve current problems more quickly and effectively. Identifying specific challenges and focusing on them in a consistent and structured manner results in achieving greater treatment gains and achieving them in a shorter period of time than in traditional talk therapy.
CBT is Active
Cognitive behavioral therapy allows you and your therapist to work as a team, collaborating to solve problems. Rather than waiting for problems to get better after talking about them repeatedly from week to week, you can take an active role in your own treatment, using self-help assignments and CBT tools between sessions to speed up the process of change. Each session is focused on identifying ways of thinking differently and unlearning unwanted reactions.
CBT is Brief
CBT is a time-limited therapy, meaning once you feel significant symptom relief and have the skills you need for success, treatment can end. This makes CBT significantly shorter in duration than traditional talk therapy, which can last years. Many people finish CBT after just a few months of therapy sessions.
However, not everyone makes significant progress in a short time; some people may need additional therapy to reduce symptoms and create lasting change. Those with serious, chronic psychological problems may need anywhere from six months to several years of treatment. However, even in these cases, CBT is generally more effective and has a shorter duration than traditional talk therapy.
CBT is Well-Researched
The most widely researched therapy that exists, over 2,000 studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of CBT for numerous psychological and medical problems. It is one of the few therapies that is scientifically proven to be effective for most problems. For more information on the kinds of problems CBT can be used to treat, explore this site using the navigation bar at the top. Follow this link to a chart comparing the effectiveness of CBT to other treatments.
CBT is Supportive
Making big changes can be difficult. Cognitive behavioral therapists take this very seriously and are dedicated to helping you along this process at your own pace, offering CBT tools in an environment of warmth and caring. Relying on the foundation of a supportive relationship, you'll feel more comfortable stepping outside of your comfort zone to achieve their goals.
Who You’ll Work With: Our Team of Psychologists
You’ll work with doctoral-level psychologists who specialize in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Los Angeles and provide expert CBT telehealth across California. Many of us serve on faculty at top graduate psychology programs and train doctoral-level therapists in evidence-based care, including CBT, ACT, DBT, and mindfulness-based therapies.
Our team holds advanced training in the gold-standard protocols you’re seeking: ERP for OCD, CBT-I for insomnia, Behavioral Activation and Cognitive Therapy for depression, PE/CPT for PTSD and trauma, IBCT for couples, and adult ADHD assessment with executive-skills coaching.
We’re collaborative and practical. From day one, you’ll get a clear plan, focused weekly actions, and steady feedback—so you know what’s working and you can see progress, session by session.
Match with an expert and start feeling better this week.
“I’ve Tried A Lot Already… How Is CBT Different?”
Mindfulness apps and self-help tips can calm you in the moment, but the gains fade fast. CBT builds habits that last.
Unstructured talk therapy can offer insight without changing behavior, while CBT adds targeted practice and real-time feedback so life actually shifts.
Medication can reduce symptoms, but it may not break the cycle. CBT teaches skills that keep working, with or without meds.
Sleep “hygiene” checklists are generally helpful but are no match for insomnia. CBT for Sleep Problems (CBT-I) retrains your sleep system with a step-by-step, data-driven plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Cognitive Behavioral Therapy work online?
Yes. CBT telehealth is effective for anxiety therapy, depression therapy, OCD treatment (ERP), insomnia treatment (CBT-I), PTSD treatment (PE/CPT), Adult ADHD skills, and IBCT couples therapy. We adapt exposures and practice tasks to your routine.
How long will therapy take?
It varies. Many clients see meaningful progress by weeks 4–8 with weekly sessions and brief practice. We review milestones regularly so you can see what’s changing.
Do I need medication?
Not necessarily. CBT helps with or without medication. We collaborate with prescribers if you’re on meds or considering them.
Can I use my insurance?
We’re private-pay and provide out-of-network (OON) superbills so you can seek reimbursement directly from your insurer if eligible.
Same-Week Appointments Available Now. Start Feeling Better This Week
No pressure • HIPAA-compliant • Warm referrals if we’re not the right fit
Find a CBT Therapist Today
Get Help Now
Taking the first step toward better mental health can feel daunting, but reaching out for support is always the right decision. At Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Los Angeles, our compassionate team of expert psychologists is here to guide you through evidence-based treatments tailored to your needs. Whether you’re struggling with anxiety, depression, relationships, or other challenges, we’re ready to help you regain control and build a healthier, more balanced life. Don’t wait—your path to wellness begins with a simple call or message today.
Trusted Therapists at CBT LA
Finding a trusted mental health professional to have an open and honest working relationship is key when starting any form of psychological treatment. Our therapists are highly trained in the field of psychology, with specialized expertise in CBT. Bringing with them a wealth of knowledge and experience, our psychologists are kept up to date with the most current CBT methods to provide you with the highest level of care possible.
Break out of Unhelpful Patterns Today
If you or someone you know is struggling, CBT might be a great way to put into action better ways of coping for creating a more fulfilling life. We at Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Los Angeles invite you to break out of that cycle now by taking the first step: reach out today to schedule your first session with the right therapist for you!
Begin your path to lasting results.
Medically Reviewed by Albert Bonfil, PsyD
*Sources for Headline Claims
Agras, W. S., Walsh, B. T., Fairburn, C. G., Wilson, G. T., & Kraemer, H. C. (2000). A multicenter comparison of cognitive-behavioral therapy and interpersonal psychotherapy for bulimia nervosa. Archives of General Psychiatry, 57(5), 459–466.
Centre for Addiction and Mental Health. (n.d.). Cognitive-behavioural therapy: An information guide.
Shedler, J. (2010). The efficacy of psychodynamic psychotherapy. American Psychologist, 65(2), 98–109.
Carpenter, J. K., Andrews, L. A., Witcraft, S. M., Powers, M. B., Smits, J. A. J., & Hofmann, S. G. (2018). Cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety and related disorders: A meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Depression and Anxiety, 35(6), 502–514.
Hofmann, S. G., Asnaani, A., Vonk, I. J., Sawyer, A. T., & Fang, A. (2012). The efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy: A review of meta-analyses. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 36(5), 427–440.
Mayo-Wilson, E., Dias, S., Mavranezouli, I., Kew, K., Clark, D. M., Ades, A., & Pilling, S. (2014). Psychological and pharmacological interventions for social anxiety disorder in adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. The Lancet Psychiatry, 1(5), 368–376.
Norton, P. J., & Price, E. C. (2007). A meta-analytic review of adult cognitive–behavioral treatment outcome across the anxiety disorders. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 195(6), 521–531.
Tolin, D. F. (2010). Is cognitive–behavioral therapy more effective than other therapies? A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 30(6), 710–720.
**Sources for the CBT Outcomes Graph
Barlow, D. H., Gorman, J. M., Shear, M. K., & Woods, S. W. (2000). Cognitive-behavioral therapy, imipramine, or their combination for panic disorder: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA, 283(19), 2529–2536.
Foa, E. B., Liebowitz, M. R., Kozak, M. J., Davies, S., Campeas, R., Franklin, M. E., … Tu, X. (2005). Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of exposure and ritual prevention, clomipramine, and their combination in the treatment of obsessive–compulsive disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(1), 151–161.
Heimberg, R. G., Liebowitz, M. R., Hope, D. A., Schneier, F. R., Holt, C. S., Welkowitz, L. A., … Bruce, T. J. (1998). Cognitive behavioral group therapy vs phenelzine therapy for social phobia: 12-week outcome. Archives of General Psychiatry, 55(12), 1133–1141.
Loerinc, A. G., Meuret, A. E., Twohig, M. P., Rosenfield, D., Bluett, E. J., & Craske, M. G. (2015). Response rates for CBT for anxiety disorders: Need for standardized criteria. Clinical Psychology Review, 42, 72–82.
Simpson, H. B., Foa, E. B., Liebowitz, M. R., Huppert, J. D., Cahill, S., Maher, M. J., … Franklin, M. E. (2008). A randomized, controlled trial of cognitive-behavioral therapy for augmenting pharmacotherapy in obsessive–compulsive disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry, 165(5), 621–630.
Stanley, M. A., Wilson, N. L., Novy, D. M., Rhoades, H. M., Wagener, P. D., Greisinger, A. J., … Kunik, M. E. (2009). Cognitive behavior therapy for generalized anxiety disorder among older adults in primary care: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA, 301(14), 1460–1467.
For more information: New York Times Article: "Evidence That Therapy Works"
Information about different cognitive behavioral therapy exercises.