CBT for Low Self-Esteem and Improving Confidence
Build Real Confidence With a Clear, Structured CBT Plan
Our expert therapists use targeted CBT strategies to quickly reduce self-criticism, perfectionism, and overthinking.
See what an evidence-based CBT approach would look like for you.
When Feeling “Not Enough” Becomes a Way of Life
A client once told me that every morning felt like opening her laptop to find a new list of ways she had failed. The list wasn’t real, of course. It lived in her mind. But she felt accountable to it. Did she answer emails fast enough? Did someone misread her tone in yesterday’s meeting? Did her friends secretly think she was awkward? She never had evidence for any of this, but the questions chased her from task to task.
If you’ve ever lived inside a loop like this, you know how absorbing it can be. You can hold a successful job, maintain relationships, hit deadlines, and still feel as if you’re running on a kind of self-doubt autopilot. It’s confusing. How can someone capable in so many ways feel so unsure on the inside?
This is one of the quiet puzzles of low self-esteem. It doesn’t always look like visible struggle. It often hides in people who are outwardly steady, responsible, and high performing. And because they’re functioning, they often tell themselves their pain doesn’t count.
At Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Los Angeles, we see this pattern every week. People who believe everyone else has a stronger internal compass. People who assume confidence is something they somehow missed out on. People who wonder whether they’re the one exception that cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can’t help.
Before we go any further, let’s pause here. If you recognize these patterns, your suffering is real. And you deserve support.
What Is CBT for Low Self-Esteem?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for low self-esteem helps you understand and change the patterns of thinking, feeling, and behavior that keep self-doubt alive. It teaches practical skills for identifying self-critical thoughts, reducing avoidance, taking small confidence-building actions, and relating to yourself with more flexibility and compassion. CBT is structured, collaborative, and usually time-limited, with modest daily practice and steady tracking of progress.
How Low Self-Esteem Shows Up in Daily Life
Low confidence often announces itself in quiet ways rather than dramatic ones. It’s not the loud, obvious kind of distress. It’s more like a subtle gravitational pull that shapes your choices.
Common patterns include:
1. You expect yourself to “get it right” the first time.
Making a mistake doesn’t feel like a normal part of learning. It feels like a sign you’re falling behind others. Even small errors activate harsh self-judgments.
2. You replay conversations long after they end.
You wonder whether you sounded odd, missed a cue, or revealed something embarrassing. You analyze your tone, your timing, even your text punctuation.
3. You take on more work than you have capacity for.
Not because you want to, but because it feels safer than saying no. You fear being seen as incapable or unreliable, so you overextend until you’re exhausted.
4. You avoid opportunities that would help you grow.
This might be applying for a promotion, speaking up in meetings, joining social activities, or trying something new. Avoidance protects you in the short term but shrinks your world over time.
5. You feel you’re “fine” because you’re functioning.
People with low self-esteem often tell themselves, “Other people have it worse.” This is a subtle way of dismissing real suffering.
6. You feel anxious and down without a clear trigger.
Low self-worth and mood often intertwine. People with depression can lose interest, feel slowed down, and experience persistent negative beliefs about themselves. These patterns can overlap with low self-esteem, even if you don’t identify as depressed.
7. You can see others kindly but not yourself.
You know how to reassure a friend. You know their struggles don’t define them. But applying that same empathy to yourself feels impossibly foreign.
If these patterns feel familiar, you’re not alone. They’re incredibly common among driven, thoughtful adults who look like they have everything together from the outside.
Start Feeling Better This Week. Same-Week Sessions Available.
Why Low Self-Esteem Happens: The CBT View
Most people assume confidence is a trait. Something you either inherited or didn’t. But CBT views confidence as something much more malleable.
Let’s walk through the psychological process that keeps low self-esteem in place.
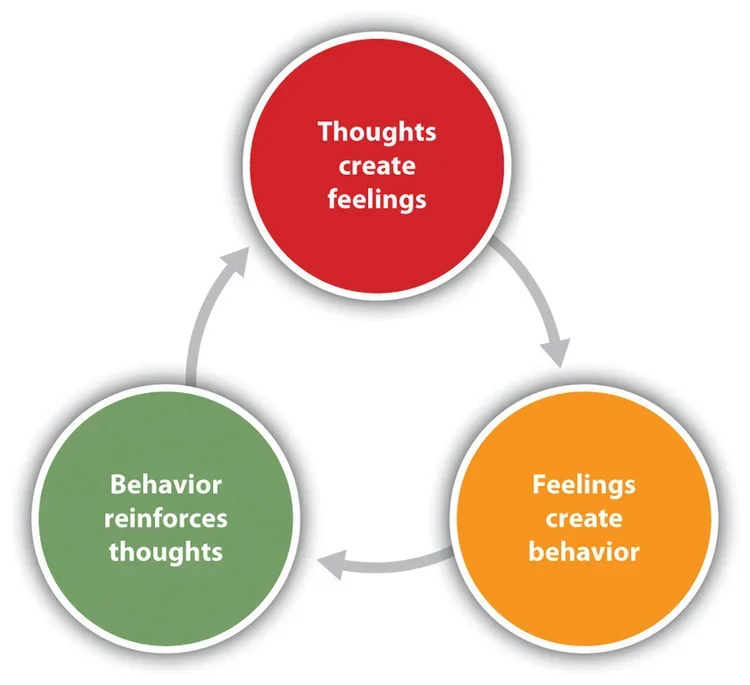
1. The cycle usually begins with automatic thoughts.
CBT uses the term “automatic thoughts” for the quick interpretations your mind generates before you even realize it. Thoughts like:
“They probably didn’t like what I said.”
“I should be doing better.”
“If I make a mistake, people will lose respect for me.”
You might not choose these interpretations. They feel instinctive. Over time, they create a sense of who you are.
2. Thoughts shape emotion.
If the thought is “I messed up again,” the accompanying emotion might be shame, anxiety, or sadness. These emotional moments are powerful because they confirm your interpretation, even when the situation was neutral.
Emotions tend to narrow our focus. Sadness can make you withdraw. Anxiety makes you scan for threats. This becomes a lens you see through, not just a passing feeling.
3. Emotions lead to avoidance.
Avoidance is one of the most counterintuitive patterns in psychology. We avoid the things that trigger anxiety or shame because avoidance feels like relief. But in the long term, it reinforces the very beliefs we fear.
If you avoid speaking up in a meeting, you never get the corrective experience that your voice is welcome. If you avoid letting people get close, you never learn that connection can be safe.
Avoidance creates the illusion that you’re protecting yourself, but it quietly locks the old beliefs in place.
4. Over time, these loops solidify into identity-level beliefs.
You start thinking:
“Maybe I’m just not confident.”
“Maybe I’m too sensitive.”
“Maybe something is wrong with me.”
These feel like facts rather than habits of mind.
5. The ACT perspective adds another layer:
A form of CBT, Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), teaches you to notice these thoughts as events in the mind rather than literal truths. “I’m a failure” becomes “I’m having the thought that I’m a failure.” This shift loosens the grip of self-judgment, even before anything else changes.
When CBT and ACT come together, you begin to see the whole system. Confidence was never a trait. It was a pattern. And patterns can be changed.
How CBT Helps Improve Confidence and Self-Esteem
So what does it look like to actually change these patterns?
CBT Offers a Clear, Structured Framework
You and your therapist collaborate on a specific plan for your goals.
Sessions are typically weekly for 50 minutes.
We use brief questionnaires and 0–10 ratings to track progress.
Around weeks four to six, we review what’s shifting and revise the plan if needed.
Treatment is active. Practical. Focused. Unlike unstructured “talk therapy,” CBT gives you a map:
1. Psychoeducation: Understanding the Cycle
We start by mapping how thoughts, emotions, physical sensations, and behaviors interact. When you can see the cycle clearly, you gain leverage over it.
2. Cognitive restructuring: Changing the story
Cognitive restructuring doesn’t mean forcing yourself to think positively. It means examining the evidence for your self-critical beliefs, considering alternative perspectives, and practicing more flexible interpretations.
We often use gentle thought records or brief “thinking trap” check-ins to identify patterns like “catastrophizing” or “mind-reading.”
3. Behavioral experiments: Testing the fear
One of the most powerful parts of CBT involves trying small, strategic actions that challenge your core beliefs.
For example:
Speaking once in a meeting and observing what actually happens
Asking a clarifying question without over-preparing
Sending an email without rereading it ten times
Letting yourself rest without guilt and noticing whether anything “falls apart.”
These experiments reveal that the feared outcomes rarely occur, which weakens old beliefs.
4. Reducing avoidance and safety behaviors
Avoidance is not just skipping big things. It can be tiny habits that keep you stuck, such as:
Overthinking before taking action
Excessive reassurance-seeking
Always deferring to others
Hiding your preferences
Editing your personality to avoid negative judgment
CBT helps you notice and reduce these habits in small, manageable ways and learn to face your fears with exposure therapy.
5. Skills training for emotion regulation
Borrowing from Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) and mindfulness-based CBT, we teach:
Grounding techniques
Distress tolerance tools
Nonjudgmental present-moment awareness
Strategies to approach discomfort with steadiness rather than panic
These skills help you stay regulated while practicing new behaviors.
6. ACT-based work on values
Confidence is rarely the final goal. Most people want confidence because it helps them pursue the life they care about. ACT helps you identify what matters: connection, creativity, leadership, authenticity, and use those values as a compass.
Values allow you to act even when you’re not feeling confident yet.
Take The First Step Toward Real Progress.
What Therapy Looks Like at
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Los Angeles
People often imagine therapy as a long, meandering conversation. In our work with low self-esteem and confidence, sessions are something different. They’re structured conversations that build toward change.
A typical course of CBT at Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Los Angeles includes:
Weekly 50-Minute Sessions
We meet either in person in our Los Angeles offices or online anywhere in California. Each session has a clear focus. You might review a recent situation, practice a skill, or plan a small confidence-building experiment to try between sessions.
Measurement-Based Care
Low self-esteem doesn’t improve by guesswork. We use short, validated questionnaires to track patterns in mood, confidence, avoidance, and functioning. Regular monitoring makes progress easier to see and helps prevent discouragement, especially when emotions narrow your focus.
We review these numbers together, often around weeks four to six, to understand what’s shifting and where the plan needs adjustment. This ensures therapy doesn’t drift, something many of our clients have experienced in past treatment.
Short, Doable Practice Between Sessions
Homework is part of CBT, but not in the overwhelming way people often imagine. We often aim for 10 to 15 minutes a day, designed collaboratively so that each exercise feels realistic. Some weeks, it might be a brief thought record. Other weeks, it might be a small behavioral experiment or a mindfulness practice.
Clients often tell us that these small steps, done consistently, are where confidence starts to expand.
A Collaborative, Pacing-Sensitive Approach
People with low self-esteem sometimes worry their therapist will push them faster than they’re ready for. In reality, progress works best when it’s chosen rather than forced. We discuss pacing openly and adjust based on your comfort level, energy, and goals.
You’re never expected to leap; you’re expected to take steps. And the steps are chosen together.
Common Fears and Objections
Nearly every person who seeks help for low confidence arrives with a set of hesitations. These concerns make sense. They’re part of the very experience you’re seeking to change.
Let’s address them directly.
“What if my problem isn’t bad enough for therapy?”
Many high-functioning adults minimize their struggles. They tell themselves they’re “fine” because they can still meet deadlines and take care of others. But the emotional cost: exhaustion, self-criticism, constant pressure, can be immense.
You don’t need a crisis to deserve support. Feeling stuck is reason enough.
“What if I’m the one person therapy can’t help?”
Low self-esteem often brings a belief that you’re uniquely flawed. The irony is that this belief is one of the most universal parts of the problem. CBT doesn’t depend on you believing you can change. It simply asks that you’re willing to experiment.
Small shifts—sometimes noticeable within three to six weeks—begin to build new evidence.
“Will this work make me feel worse before it gets better?”
Trying something new can feel uncomfortable. But discomfort is not the goal; growth is. We plan each step carefully so you’re not overwhelmed. Behavioral experiments are small, controlled, and structured to produce learning, not distress.
And if something feels too much, we recalibrate.
“What if the time and cost don’t pay off?”
This is a reasonable concern, especially for people accustomed to shouldering everything themselves. CBT is intentionally efficient. It uses focused sessions, practical tools, and modest daily practice. The goal is not years of insight. It’s creating forward movement in the areas that matter most: work, relationships, decisions, and self-regard.
Clients often tell us that these shifts ripple far beyond the specific issue they came in with.
“Will my therapist judge me?”
Judgment is the last thing that helps change. What helps is curiosity. In our practice, your patterns are not seen as personal flaws but as adaptations—strategies that made sense at earlier points in your life. Therapy becomes a space to understand those strategies and gently shape new ones.
“Will I be pushed too quickly?”
CBT is structured, but not rigid. Our work is collaborative. You set the pace. We build the plan together. And we adjust it whenever needed.
Frequently Asked Questions about CBT for Low Self-Esteem
What causes low self-esteem?
Low self-esteem develops from repeated patterns of self-critical thinking, avoidance, perfectionism, and emotionally painful experiences. Over time, the brain treats these patterns as facts. CBT helps interrupt these habits and build new ones.
Why does low self-esteem feel so difficult to change?
Because the habits that maintain it—overthinking, avoidance, seeking reassurance, harsh self-judgment—offer short-term relief. But these habits prevent new evidence from forming. CBT uses small behavioral experiments and cognitive tools to create experiences that challenge old beliefs.
How long does CBT for low self-esteem usually take?
Many clients notice early changes within three to six weeks when they practice skills consistently. More complete gains often develop over a few months. Therapy is time-limited and goal-focused.
Can CBT help if I’ve tried therapy before and didn’t feel progress?
Yes. Many clients come to us after unstructured talk therapy that felt supportive but didn’t create change. CBT includes clear goals, skills, measurement, and accountability, making it particularly helpful for people who want structure.
Does this work for people who are high-functioning but feel insecure?
Absolutely. High-functioning people often hide their struggles. CBT is well-suited for people who appear confident externally but feel shaky internally.
Can I do CBT online if I live outside Los Angeles?
Yes. We offer online CBT across California. If you’re in or near Los Angeles, you can choose in-person, online, or hybrid sessions.
Will I have homework?
Yes, but it’s designed to be manageable, usually ten to fifteen minutes a day. The goal is to create steady change without adding pressure.
When to Seek Professional Help for Low Self-Esteem
You don’t need a dramatic low point to start therapy. It’s time to reach out if:
You feel overwhelmed by self-doubt.
Your inner critic runs constantly.
You avoid opportunities even when you want them.
Confidence swings with every piece of feedback.
You’re tired of working twice as hard to feel half as good.
You want to feel more grounded, less reactive, and more aligned with your values.
If you recognize yourself here, you don’t have to figure this out alone. These are exactly the patterns we help clients work through.
Get Help Now.
If you’d like structured, evidence-based help with low self-esteem or confidence, we’re here to talk. You can schedule a full intake appointment or a free fifteen-minute consultation to get a sense of how we work. There’s no pressure to commit. The goal of this first step is simply to explore whether working with a CBT therapist in Los Angeles, or online anywhere in California, feels like the right fit for you.
Most people feel nervous reaching out. You don’t need a perfect explanation of what you’re struggling with. Your first step is simply to contact us, and we’ll handle the rest together.
Confidence grows from small, steady actions. Reaching out can be your first one.
Don’t Wait. Take Back Your Life Today.
Medically Reviewed by Albert Bonfil, PsyD